System Engineering Acquisition Process: A CRM Acquisition Scenario

Article Header Image is created using AI Engine and prompt used is : “Flying car in the sky, with futuristic engineering . Conceptual art style, with a focus on light and shadow” . We appreciate the advancements in technology that enable us to bring creative ideas to life. Special thanks to the developers and researchers who contribute to these innovative tools.
The acquisition process refers to the systematic approach of acquiring a product, system, or service to meet specific needs within a system lifecycle. This includes activities such as defining requirements, selecting suppliers, establishing contracts, and ensuring that the acquired system meets the desired specifications and quality standards.
Acquisition process.
Examples are crucial for making complex information easier to understand because they turn confusing ideas into simple, real-life scenarios. When combined with images, examples help readers remember and use the information more effectively.
Example Scenario
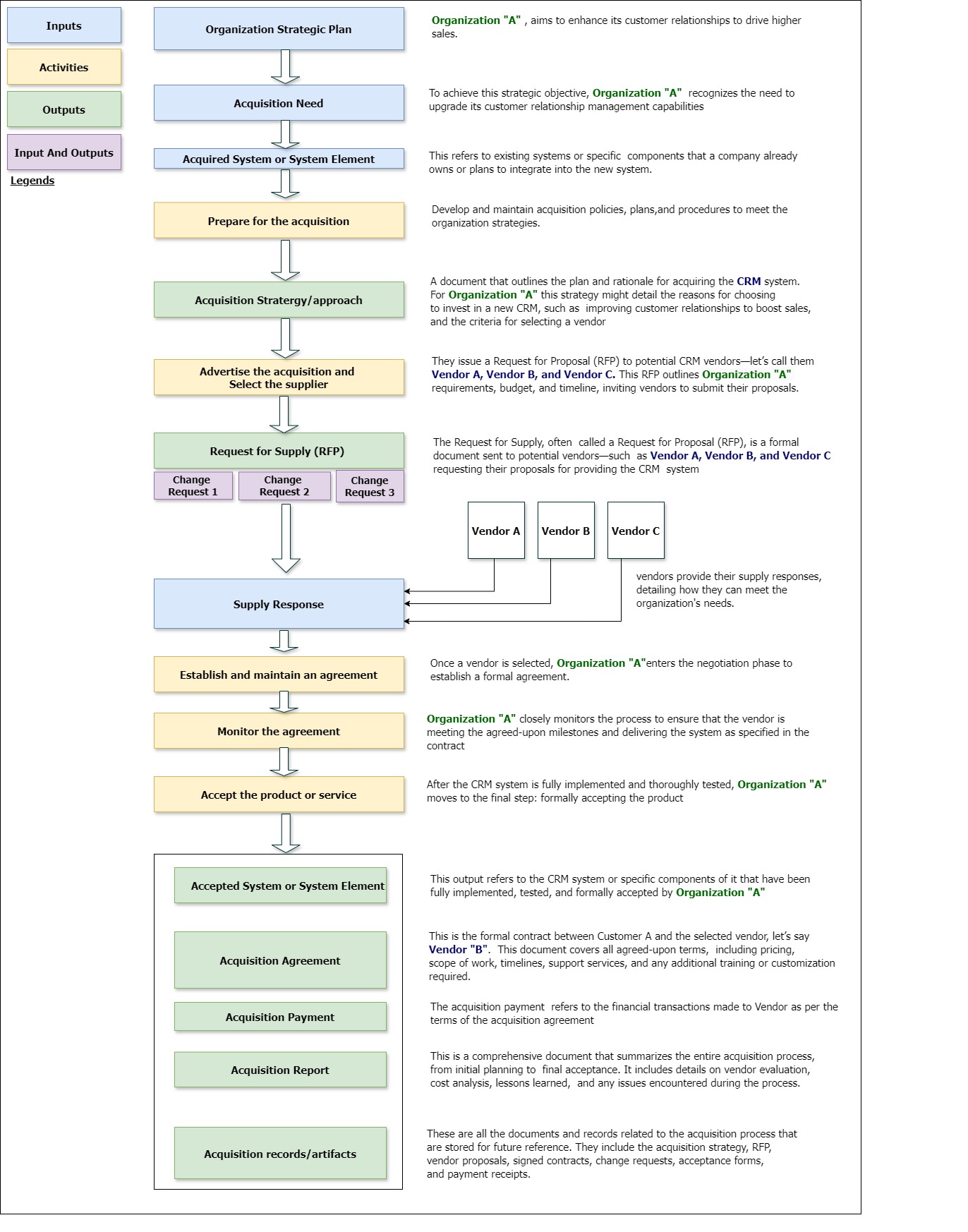
Organization “A” wants to strengthens their customer relationships to boost Sales Imagine a scenario where Organization A, aims to enhance its customer relationships to drive higher sales. As part of its Organization Strategic Plan, the company decides to prioritize improving how it interacts with and manages its customers. To achieve this strategic objective, Organization A recognizes the need to upgrade its customer relationship management ( CRM ) capabilities. This involves optimizing how they handle customer data, track interactions, and manage communications.
As a result, the company identifies a key requirement: a new CRM system that can streamline customer interactions, offer deeper insights into customer behavior, and enable more personalized marketing and sales efforts. If Organization A already has an existing CRM system or specific element/module that need to be integrated, these aspects will also be factored into the acquisition process. This strategic plan guides the development of a Request for Proposal (RFP), which will be sent to potential CRM vendors, let’s refer to them as Vendor A, Vendor B, and Vendor C. The RFP will clearly outline Organization A’s strategic goals and specify how the proposed CRM solutions should align with these objectives.
In response, the CRM vendors submit their proposals, each offering a detailed explanation of how their solution can meet Organization A’s needs. During this stage, Organization A may also adjust or change its initial requirements based on internal feedback or evolving market conditions. When assessing these proposals, the company will prioritize vendors whose solutions best support its goal of improving customer relationships.
Visual Guide to the Acquisition Process - CRM Acquisition
Selecting the Right Supplier
When selecting the right supplier for a manufacturing project, it’s crucial to follow a structured checklist to ensure compatibility and reliability. For instance, consider a company looking to source high-precision components for an advanced train manufacturing line. The company first defines its requirements by detailing the exact specifications for the components, including material strength, dimensional tolerances, and production volume. They then research potential suppliers, evaluating their experience in producing similar components and checking their reputation through industry reviews and certifications like ISO 9001.
The next step involves assessing the suppliers’ capabilities, such as their production capacity and technology for machining high-tolerance parts. Financial stability is reviewed by analyzing credit reports and pricing structures to ensure they fit within the project’s budget. Compliance with industry regulations and having adequate insurance coverage is also crucial to mitigate risks.
Logistics play a significant role; the company considers suppliers’ delivery times and proximity to reduce lead times and shipping costs. Effective communication and support are evaluated by assessing the suppliers’ responsiveness and customer service quality. Contract terms are scrutinized to ensure they are fair and flexible enough to accommodate any potential changes in order volume. Finally, the company tests sample components to verify their performance and reliability before making a final decision. By following this checklist, the company ensures that the selected supplier meets all technical, financial, and logistical requirements, thereby securing a successful partnership for its manufacturing needs.
Suppliers Responding to Acquisition Requests
When responding to an acquisition request, suppliers need to follow a detailed checklist to ensure their proposal meets all requirements and stands out. For example, consider a supplier responding to a Request for Quotation (RFQ) for high-precision components needed for an aerospace project. The supplier begins by thoroughly reviewing the RFQ to understand the specific technical specifications, delivery schedules, and budget constraints. They prepare a comprehensive proposal, detailing the technical capabilities of their components, a clear pricing structure, and a realistic timeline for delivery.
To ensure compliance, the supplier includes documentation showing that their components meet all relevant industry regulations and standards, along with copies of necessary certifications. They also provide proof of financial stability and insurance coverage to address any legal and financial concerns. The proposal includes case studies from similar projects and, if requested, samples of the components for evaluation.
Throughout the process, the supplier maintains accurate contact information for follow-up inquiries and adheres to the submission deadline. They conduct a thorough review of their proposal to verify accuracy and completeness before submission. By following this checklist, the supplier ensures that their proposal is not only thorough and compliant but also positioned to meet the acquisition request effectively, thereby enhancing their chances of securing the contract.
